Understanding Gum Health: How to Prevent and Treat Gum Disease
When it comes to oral health, most of us focus on keeping our teeth clean and cavity-free. However, gum health is equally important, and neglecting it can lead to serious problems such as gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. In the UK, nearly half of adults over 30 have some form of gum disease, making it a common issue that’s often overlooked. Healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile, and understanding how to prevent and treat gum disease is essential for maintaining overall oral health.
In this blog, we’ll explore what gum disease is, the signs to watch for, and the best ways to keep your gums healthy and strong.
What Is Gum Disease?
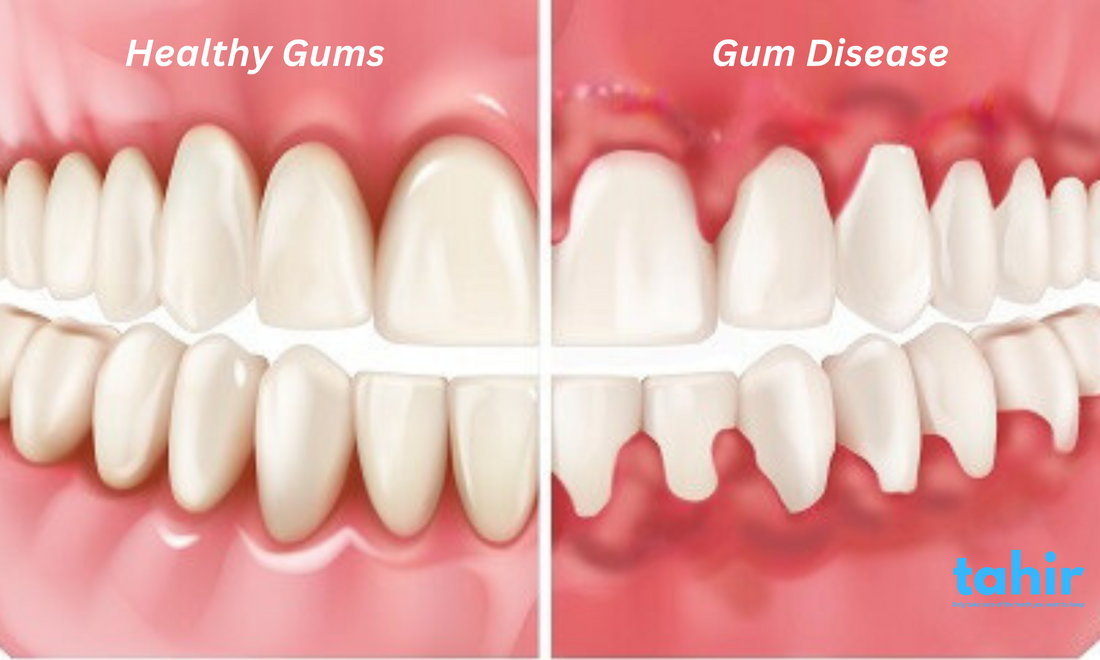
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It typically starts with gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease that causes redness, irritation, and bleeding. If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into a more serious condition called periodontitis, which can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth, eventually leading to tooth loss.
Signs of Gum Disease
Early detection of gum disease is key to preventing it from progressing. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Red, Swollen Gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pink. If they appear red, swollen, or puffy, this could be a sign of inflammation caused by gum disease.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing are one of the earliest signs of gingivitis. It’s important not to ignore bleeding gums, even if the bleeding seems minor.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) or a bad taste in your mouth can be a sign of gum infection.
- Receding Gums: If your gums are pulling away from your teeth, creating a “longer” tooth appearance, this could be a sign of gum recession, which often indicates periodontitis.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced gum disease can cause teeth to become loose or even fall out due to the destruction of bone and gum tissue.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek advice from your dentist as soon as possible.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If plaque isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which is much harder to remove and can lead to gum irritation and infection. Other factors that can contribute to gum disease include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque and bacteria to build up on the teeth and gums.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease, as it weakens the immune system and makes it harder for your gums to heal.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to gum disease due to genetic factors, making it especially important to stay on top of gum care.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including gum disease.
- Stress: High stress levels can weaken your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off gum infections.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
The good news is that gum disease is largely preventable with a consistent oral care routine and regular dental checkups. Here’s how you can keep your gums healthy:
1. Brush Twice a Day
Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste is essential for removing plaque. Make sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush, as brushing too hard with stiff bristles can damage your gums. Pay special attention to the gum line, as this is where plaque tends to build up.
Tip for Readers: Electric toothbrushes are highly effective at removing plaque and maintaining gum health. Many UK brands offer electric brushes with timers and pressure sensors to help prevent over-brushing.
2. Floss Daily
Flossing is crucial for removing food particles and plaque from between the teeth, where a toothbrush can’t reach. For best results, floss gently along the sides of each tooth and under the gum line.
Tip: If flossing feels tricky, try using interdental brushes or floss picks, which are widely available in UK supermarkets and pharmacies.
3. Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash
Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the bacteria that cause gum disease. Choose a mouthwash with ingredients like chlorhexidine or essential oils to target bacteria and keep your mouth fresh.
Bonus: Look for mouthwashes that are approved by the British Dental Health Foundation, ensuring they meet UK standards for gum health.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease, as it weakens your body’s ability to fight infections and heal from gum inflammation. Quitting smoking not only benefits your gums but also improves your overall health.
Tip: The NHS offers free support to help you quit smoking, including local stop-smoking services and nicotine replacement therapies.
5. Regular Dental Checkups
Visiting your dentist regularly is vital for preventing and detecting gum disease early. Your dentist can spot the signs of gingivitis before it becomes more serious and can provide professional cleaning to remove tartar and plaque buildup.
UK Tip: Dental checkups are available for free under the NHS for children and teenagers under 18, and for pregnant women. Adults can also access NHS dental care, although private care may be quicker if waiting lists are long.
How to Treat Gum Disease
If you’ve already developed gum disease, don’t worry — it’s treatable, especially when caught early. Here are the most common treatments:
1. Professional Cleaning
In the early stages of gum disease (gingivitis), a professional dental cleaning can remove tartar and plaque build-up, giving your gums a chance to heal. Your dentist or dental hygienist may perform a “scaling” procedure to remove the tartar from above and below the gum line.
2. Root Planing
For more advanced gum disease (periodontitis), your dentist may recommend root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that smooths the surfaces of your tooth roots to help gums reattach and heal.
3. Medications
In some cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial mouthwashes to help control the infection and inflammation.
4. Surgical Treatments
For severe cases of gum disease, surgical options like flap surgery or bone grafts may be necessary to restore damaged gum and bone tissue.
Conclusion
Caring for your gums is an essential part of maintaining good oral health. By adopting a consistent oral hygiene routine, visiting your dentist regularly, and avoiding habits that increase your risk, you can prevent gum disease and keep your gums in top shape.If you’re concerned about your gum health or want advice on the best products for gum care, explore our range of sustainable, high-quality oral care products. At Tahir Oral Care, we’re committed to helping you achieve a healthy smile while taking care of the planet. Keep your gums happy, and your smile will follow!
